Describe the Movement of Volvox and Euglena
Volvox Spirogyra Diatoms Polysiphonia Euglena Reproduction Locomotion 8 Photosynthetic pigments Niche 22 Describe the movement of a Volvox colony and the unicellular Euglena. Why is Euglena call mixotrophic.

Protists Euglena Amoeba Paramecium Volvox
The movement of a Volvox colony seems to be a constant movement in a circularspinning motion.

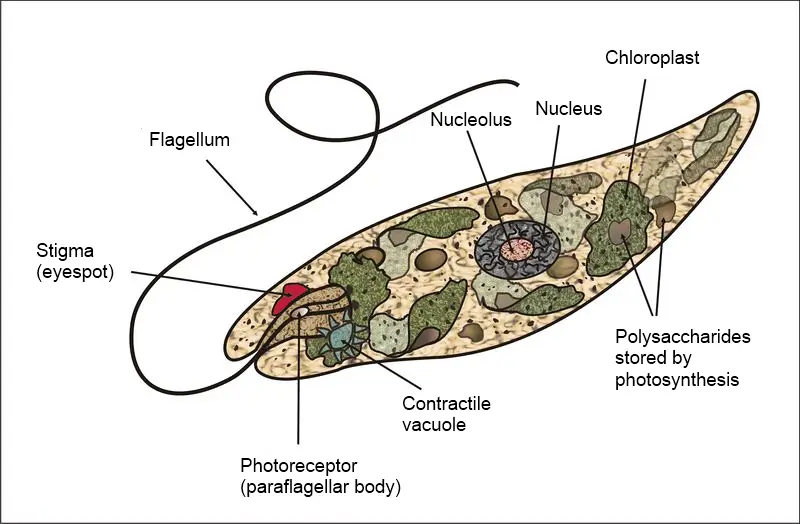
. Waste- Contractile v acuole collects excess water then squirts it out of the cell. Euglena move much more slowly than the Volvox. Thousands of cells together form colonies.
The sperm then fertilizes and produces zygotes of viable volvox. Volvox- have very large colonies. Kingdom Protista consists of diverse eukaryotic.
This lasts over winter and will germinate when spring comes. The cells divide from the parental colony and form the gonidia. There are two features on its body that facilitate in its movement.
The females develop into new spheres of the gonida developing into two pairs of eggs. 21 Complete the table below. How could you tell.
This helps them to move forward spiraling through the water around an invisible axis in pursuit of food. They seem to be spinning rather quickly until they bump into another Volvox then they seem to slow down but still maintain the spinning motion. 5 Sketch each of the specimen.
The polar organization of algal cells is responsible for the movement of this algal species. The next that we will observe under a high power compound light microscope is the volvox. Each spore then will produce new plant animals.
Euglena has plastids and performs photosynthesis in light but moves around in search of food using its flagellum at night. Volvox Spirogyra Diatoms Polysiphonia Euglena Reproduction Locomotion 8 Photosynthetic pigments Niche 22 Describe the movement of a Volvox colony and the unicellular Euglena. Describe the movement of a Euglena.
Leeuwenhoek was the first scientist to observe them in 1700. Euglena is a type of euglenoid. 23 What is a mixotroph.
Autotroph Paramecium - Cilia Oral Groove through contractile vacuole. This the reason why volvox moves towards the direction of light. Paramecium generally thrusts itself forward traveling in a straight line through the water.
A plant characteristic of the euglena is that it forms a resting spore with a thick wall during autumn. How do Euglena satisfy their nutritional requirements. They possess the characteristic features of plants and animals.
The most important is the flagellum which is a long whip-like appendage attached to the body. This organelle helps the cell remove access water and without it the Euglena could take in so much water due to osmosis that the cell could explode. Describe what the scientist should look for and how to determine plant or animal.
Rhodophyta- a eukaryotic cell that lacks a flagella. Euglenoids are unicellular microorganisms that have a flexible body. Euglena - Flagella Photosynthesis Autotroph A scientists is looking at a cell to determine if it is a plant or an animal cell.
Euglena move from one place to another like an animal. Euglena change their shape in order to move. A large eye-spot is present in the anterior pole which enable the cells to detect light.
Describe the different forms of movement and locomotion in the Euglena They move both by using the flagellum to project it forward and also with worm like contractions when the flagellum is not being used. Volvox is widely studied to understand the process of morphogenesis. When they manufacture their own food they have to move to such an area where they can receive required amount of sunlight.
4What domain do these cells belong to. There are around 1000 species of Euglena found. What structure s found on the Euglena is used for locomotion.
3 How would you describe the movement of each organisms. They are very spherical. Volvox EUGLENA Single-celled Protists that lives in fresh water.
There are around 500 to 60000 cells in each colony of volvox. Volvox is a genus of green algae containing around 20 species of freshwater algae. Expert Answer 100 5 ratings Euglena moves with the help of flagella a hair- like structure which functions as a motor f.
However it is capable of changing its direction when it comes in contact with a. Captures food by eating other organisms Has chlorophyll More Info on Euglena Eyespot helps it sense light. Movement by a f lagella video More Info on Euglenas.
Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Volvox Tardigrades and Daphnia Answer the following questions. In contrary to the anterior side the posterior pole participates in reproduction process. Volvox - Flagella Photosynthesis.
The key difference between volvox paramecium and euglena is that volvox is a green alga that lives as colonies in freshwater while paramecium is a ciliate protozoan that resembles the shape of a shoe and euglena is a single-celled flagellate eukaryote which has both plant and animal features. Euglena move by a flagella which is a long whip-like structure that acts like a little motor. Nutrition is holophitic making use of photosynthesis.
1 Which of these organisms would move fastest in the absence of methyl cellulose.

The World Of Amoeba Euglena Paramecium And Volvox Cells Ppt Video Online Download
Euglena Under The Microscope Structure Morphology Classification

Amoeba Euglena Paramecia Protists Science Videos Science Lessons

Comments
Post a Comment